Introduction
The full form of PE is Polyethylene. a versatile and widely-used polymer, plays a pivotal role in our daily lives. From packaging materials to medical devices, its applications are diverse and expansive. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of polyethylene, exploring its structure, properties, uses, manufacturing process, recycling, and more.
What is Polyethylene?
Polyethylene is a thermoplastic polymer composed of ethylene monomers. Its molecular structure consists of long chains of repeating ethylene units, creating a flexible and durable material. As one of the most commonly produced plastics, polyethylene is recognized for its resilience and versatility.

Polyethylene Structure
The structure of polyethylene is relatively simple yet highly effective. It is a linear polymer, meaning the ethylene monomers are connected in a straight chain, allowing for flexibility and ease of processing. The absence of branching enhances its strength and durability.
Types of Polyethylene
Polyethylene is synonymous with plastic. It is classified into different types based on its density
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE) stands out for its robustness and durability, making it ideal for applications demanding strength.
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) offers unparalleled flexibility and versatility
- Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) strikes a balance, providing a mix of strength and flexibility for a wide range of uses.
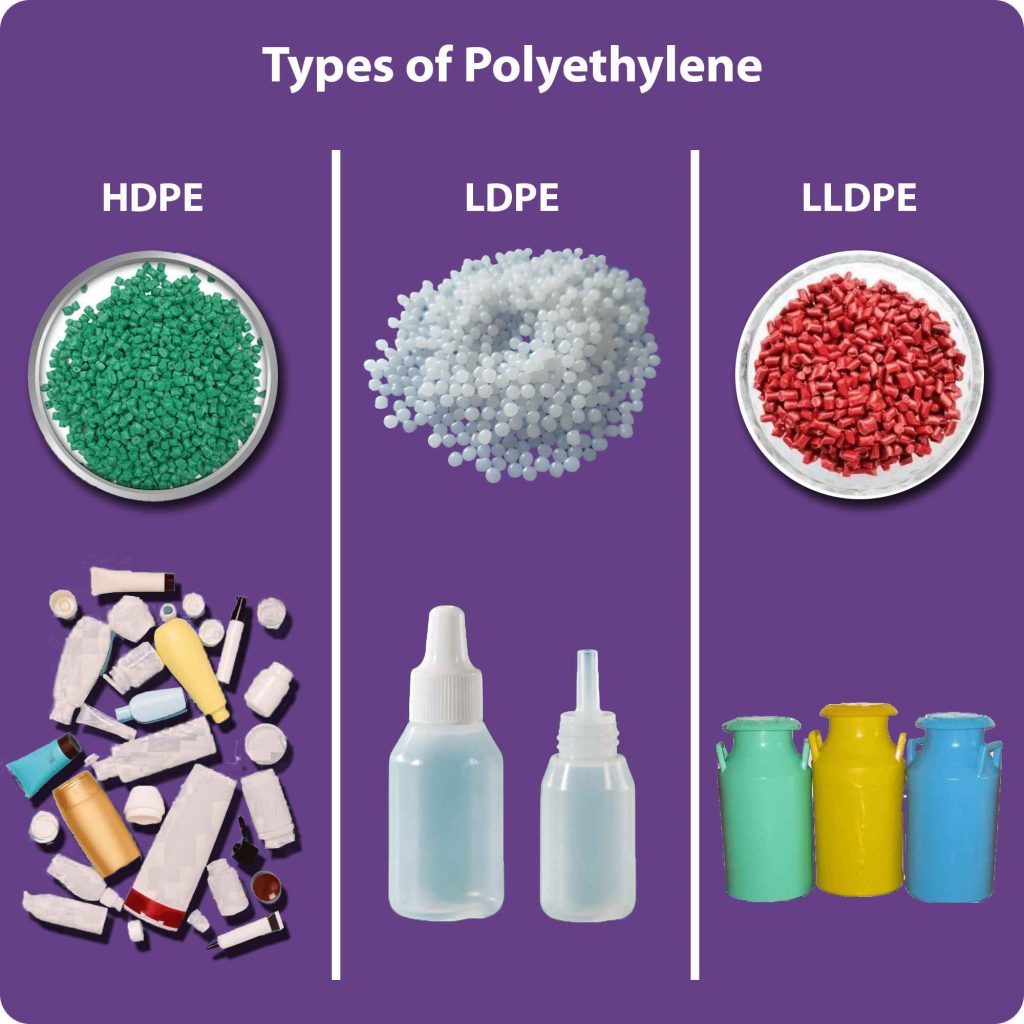
Each type has unique properties, making them suitable for specific applications
Polyethylene Uses
The applications of polyethylene are vast and varied. From everyday items like plastic bags, bottles, and containers to more specialized uses in industries such as agriculture, healthcare, and construction, polyethylene proves its versatility. Its lightweight nature, resistance to chemicals, and durability make it an ideal choice in diverse fields.
Polyethylene finds applications in various industries. It is used in packaging materials, pipes, medical devices, toys, and even clothing. Its adaptability and cost-effectiveness contribute to its widespread usage.
Polyethylene’s impermeability and resistance to external elements make it an excellent choice for covers and films. Whether used in agriculture for greenhouse films or as protective covers, polyethylene ensures durability and reliability.

Polyethylene sheets are commonly used for various applications, including construction, agriculture, and packaging. Their flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals make them a preferred choice.
Polyethylene bags are prevalent in daily life, serving as packaging for groceries, retail products, and more. Their lightweight nature, ease of production, and cost-effectiveness contribute to their widespread use
Polyethylene Properties
Polyethylene is celebrated for its exceptional properties. It is lightweight, resistant to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. Its excellent electrical insulating properties, low friction, and ease of processing make it a material of choice in many industries
How is Polyethylene Made
Polyethylene is produced through the polymerization of ethylene monomers. The process involves using catalysts and high-pressure or low-pressure conditions, depending on the desired type of polyethylene.
Polyethylene Melting Point
The melting point of polyethylene varies with its type. HDPE, LDPE, and LLDPE have melting points ranging from 120 to 137 degrees Celsius. This characteristic allows for easy processing and molding.
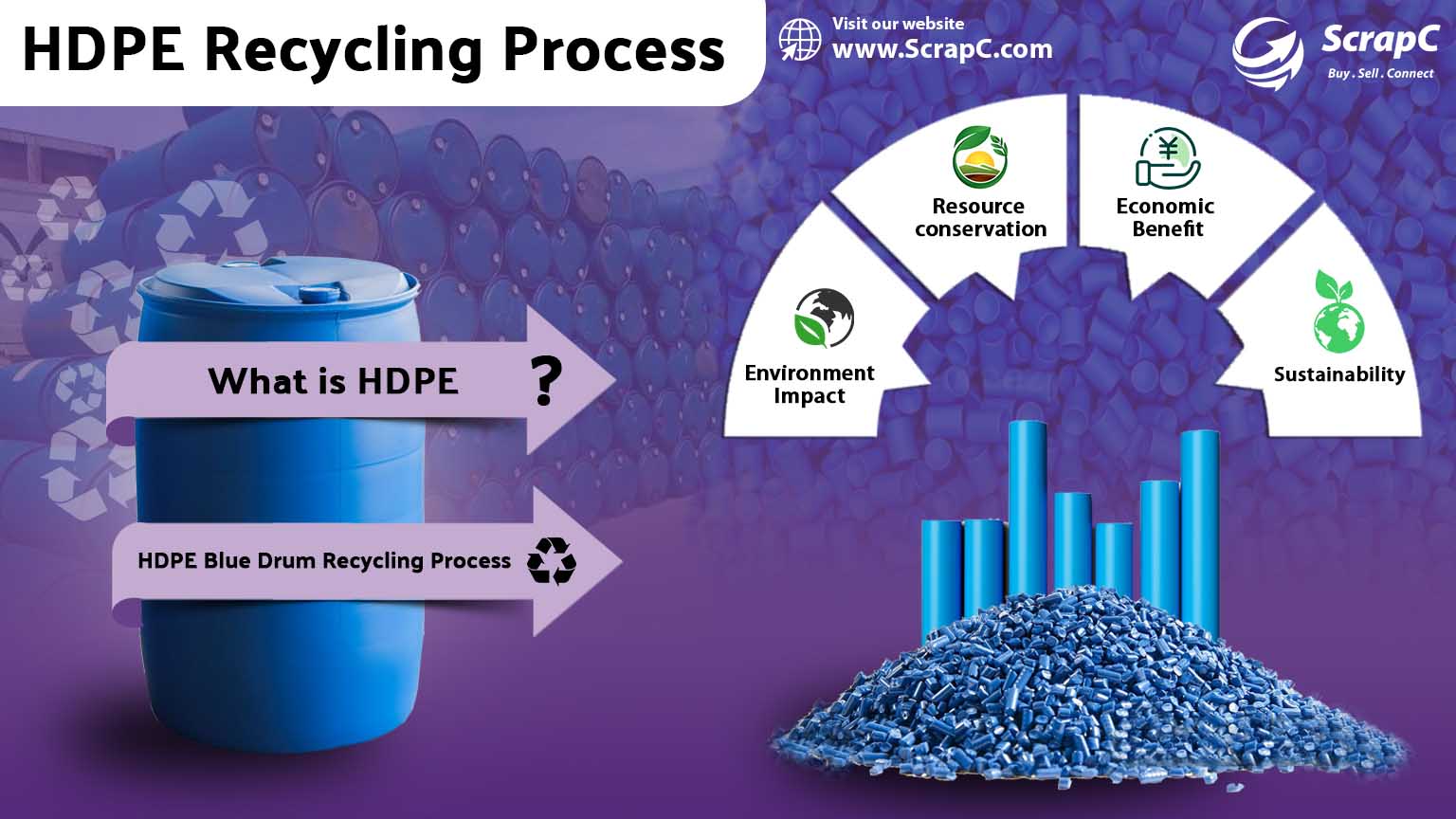
Polyethylene Recycling
Polyethylene is recyclable, contributing to sustainable practices. Recycling involves collecting, cleaning, and processing used polyethylene products into new materials, reducing environmental impact.
Polyethylene Packaging
The use of polyethylene in packaging is ubiquitous. Its durability, flexibility, and resistance to external factors make it an ideal material for various packaging applications, from food containers to industrial packaging.
History of Polyethylene
Polyethylene’s history dates back to the early 20th century. It was first synthesized in 1933 by researchers Reginald Gibson and Eric Fawcett at the Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) in England. Its commercial production began in the 1950s, revolutionizing the plastics industry.

Polyethylene Examples
Examples of polyethylene products include plastic bags, bottles, containers, pipes, medical devices, toys, and agricultural films. Its adaptability makes it a staple in numerous everyday items.
Polyethylene Formula
The chemical formula for polyethylene is (C2H4)n, where “n” represents the number of repeating ethylene units in the polymer chain. The monomer of polyethylene is ethylene (C2H4)
Conclusion
Polyethylene stands as a cornerstone in the world of plastics, demonstrating unparalleled versatility and adaptability. From its straightforward molecular structure to its myriad applications, polyethylene continues to shape industries and everyday life. Understanding its properties, uses, and manufacturing process sheds light on the importance of this remarkable polymer in our modern world.