Introduction
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a versatile material with a wide range of applications. In this blog, we’ll explore the properties, uses, and the manufacturing process of PVC.
What is PVC ?
PVC stands for Polyvinyl Chloride, which is a synthetic plastic polymer. It is a versatile and widely used thermoplastic material known for its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. PVC is produced through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers.

The Harmonized System Nomenclature (HSN) code for PVC pipes is 3917.
PVC Structure and Formula
PVC has a linear structure, consisting of repeating vinyl chloride units. Its chemical formula is (C2H3Cl)n, where ‘n’ represents the number of repeating units in the polymer chain.
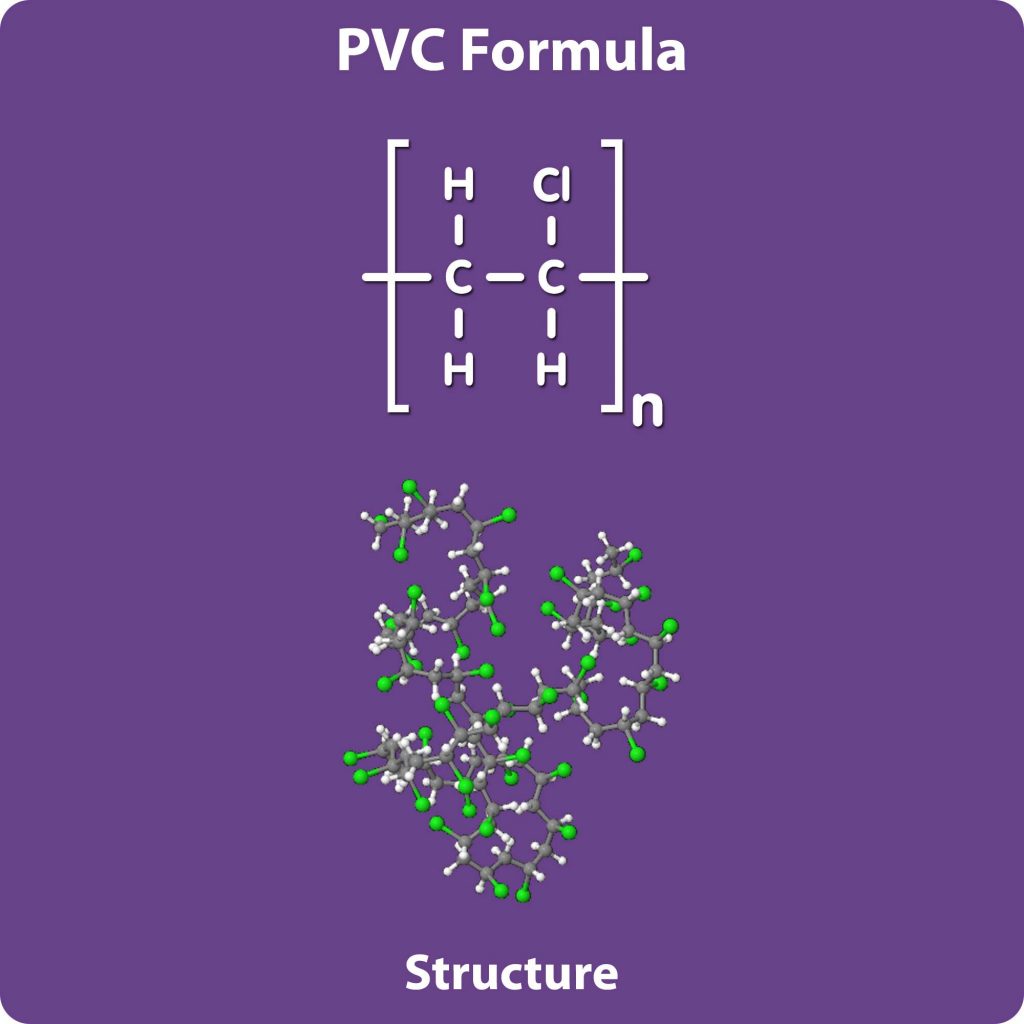
The monomer of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is vinyl chloride. PVC is created through the polymerization of vinyl chloride molecules. Vinyl chloride is a colorless gas with the chemical formula CH2=CHCl.
PVC Properties
- Density:
PVC is a lightweight material with a density ranging from 1.3 to 1.45 g/cm³. - Melting Point:
The melting point of PVC is approximately 212°C (414°F).
Versatility:
PVC is highly versatile, offering a balance of strength, durability, and flexibility.
Types of PVC
There are various types of PVC, including rigid PVC (uPVC) and flexible PVC (soft PVC). Each type has specific applications based on its properties.
- PVC Pipes:
Used extensively in plumbing due to its corrosion resistance and durability. - Construction Materials:
PVC is used in doors, windows, and siding for its weather-resistant properties.
Electrical Insulation:
Widely employed in electrical cables and insulation due to its excellent insulating capabilities.
PVC Manufacturing Process
The production of PVC involves the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers. The resulting polymer is then processed into various forms, such as sheets, pipes, or compounds. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is synthesized through a multi-step manufacturing process, commencing with the extraction of vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) from ethylene or acetylene. This monomer then undergoes polymerization, commonly through suspension polymerization, forming PVC particles. The reaction is facilitated by initiators and stabilizers, maintaining optimal conditions for polymer growth. After polymerization, the resulting PVC resin is purified, and various additives, such as plasticizers and stabilizers, are incorporated to enhance specific properties. The compounded PVC resin is then processed through extrusion or molding machines, and the final products are shaped, cooled, and cut to desired specifications. Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the process to ensure the end products meet industry standards.
PVC History
PVC’s development dates back to the 19th century, but large-scale commercial production began in the 20th century. Over time, it has become one of the most widely used plastics globally
Usage of PVC
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic is one of the most widely used plastics in the world due to its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some common applications of PVC plastic:
- Construction: PVC is used extensively in the construction industry for pipes, fittings, siding, roofing membranes, window frames, and flooring materials. Its excellent chemical resistance, low cost and ease of installation make it a popular choice for a variety of construction purposes.
- Packaging: PVC is used in packaging applications such as shrink-wrap film, cling film, blister packs and bottles. Its transparency, flexibility and ability to form an airtight seal make it suitable for the preservation and protection of a variety of objects.
- Electrical: PVC is commonly used in the electrical industry for insulation on wires and cables. It provides excellent electrical insulation properties, is resistant to moisture and chemicals, and helps protect wires and cables from damage.
- Automotive: PVC is used in the automotive industry for a variety of components such as door panels, upholstery, dashboard covers and wire harnesses. It offers good impact resistance, durability and can be easily molded into complex shapes.
- Medical: In the medical field, PVC is used in applications such as medical tubing, IV bags, blood bags, and medical devices. PVC’s biocompatibility, flexibility, and ability to withstand sterilization make it suitable for these medical applications.
- Consumer Goods: PVC is used in a wide range of consumer goods such as toys, furniture, shoes, inflatable structures, and household items. Its versatility, durability and ability to be molded into various shapes and colors make it suitable for manufacturing these products.
While PVC has many applications, it is important to note that its production and disposal can have environmental impacts due to the release of toxic chemicals during manufacturing and the generation of persistent pollutants when incinerated. Efforts are being made to address these concerns through better recycling methods, development of alternative materials, and the use of additives to enhance its environmental performance.

PVC Products
- PVC Sheet:
Durable PVC sheets for construction and signage, offering versatility in various applications. - PVC Pipe:
Sturdy PVC water pipes known for corrosion resistance, ensuring efficient plumbing solutions. - PVC Plastic:
Industrial-grade PVC plastic components, resilient and suitable for diverse manufacturing applications. - PVC Board:
Lightweight PVC foam boards, perfect for eye-catching displays and advertising materials. - PVC Material:
Premium PVC material, striking a balance between strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. - PVC Panel Wall:
Decorative PVC wall panels for modern interiors, providing a low-maintenance alternative to traditional coverings. - PVC Film:
Clear PVC film designed for packaging, ensuring excellent visibility and protection. - PVC Powder:
Fine PVC powder for coating applications, delivering a smooth and durable finish. - PVC Sheet Panel:
Easy-to-cut PVC sheet panels for DIY projects, ideal for creating customized surfaces and structures. - PVC Granules:
High-quality PVC granules tailored for injection molding, ensuring precision in manufacturing. - PVC Roll Sheet:
Flexible PVC roll sheets for resilient and visually appealing flooring solutions, easy to clean and maintain. - Polypropylene Rope: Durable and versatile, perfect for a wide range of applications with its strength and resistance
Polypropylene Homopolymer: Uniquely engineered for superior strength and purity, ideal for demanding applications in industries ranging from packaging to automotive components.
PVC Pipe
Sizes and Fittings
Explore a range of PVC pipe sizes and fittings tailored for diverse plumbing and construction needs. From standard diameters to specialized configurations, PVC pipes offer versatility and durability, ensuring efficient water supply and drainage systems. Complemented by a variety of fittings such as joints, elbows, and connectors, these components provide a comprehensive solution for creating reliable and customized piping networks. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, the availability of different PVC pipe sizes and fittings allows for seamless integration into various projects, contributing to the resilience and longevity of plumbing systems.
Accessories
Discover a comprehensive array of PVC pipe accessories designed to enhance the functionality and versatility of PVC piping systems. From essential components like couplings, adapters, and caps to more specialized accessories such as brackets and hangers, these additions facilitate seamless connections, transitions, and support for PVC pipes. PVC pipe accessories play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and customized plumbing solutions, allowing for easy installation, maintenance, and adaptation to diverse applications. Explore the wide range of PVC pipe accessories to optimize your piping infrastructure for durability and performance in various residential, commercial, and industrial settings
Types of PVC Pipe Fittings
PVC pipe fittings, essential for diverse plumbing needs, include Elbows for directional changes, Tees for two-way flow, and Reducers for size transitions. Couplings securely join pipes, while Adapters connect different materials. Caps and Plugs seal ends, Unions allow easy disconnection, and Crosses and Wyes facilitate branching. Ball Valves control flow, Check Valves ensure unidirectional movement, and Nipples are short connectors. Couples simplify PVC pipe connections for efficient assembly
PVC and Its Environmental Impact
While PVC has widespread applications, concerns about its environmental impact exist, leading to ongoing efforts to develop sustainable alternatives
Conclusion
Polyvinyl Chloride, with its diverse properties and applications, plays a crucial role in various industries. Understanding its structure, properties, and manufacturing process provides valuable insights into the world of PVC and its extensive uses.