In our modern world, plastic has become an integral part of our daily lives. From packaging materials to consumer products, its versatility has made it ubiquitous. In this blog, we’ll delve into the basics of plastic, its types, uses, and the intriguing process of its creation.
What is Plastic ?
Plastic is a synthetic material made from polymers—large molecules composed of repeated subunits. These polymers give plastic its unique properties, such as flexibility, durability, and moldability.

What is Polymer ?
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units called monomers. In the case of plastics, polymers are the building blocks that provide the material with its distinct characteristics.
Types of Plastic
Plastics come in various types, each designed for specific purposes. Common types include,
- Polyethylene (PE): A widely used thermoplastic, PE is known for its versatility, durability, and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging, containers, and various consumer products.
- Polypropylene (PP): As a robust and heat-resistant thermoplastic, PP is commonly employed in packaging, textiles, and automotive components, owing to its strength and resistance to chemicals.
- PVC(Polyvinyl Chloride): A versatile plastic, PVC is valued for its durability and chemical resistance, finding applications in construction, healthcare, and electrical systems.
- PET(Polyethylene Terephthalate): Recognized for its transparency, strength, and recyclability, PET is commonly used in beverage bottles, food packaging, and textile fibers.
and more.

Uses of Plastic
The versatility of plastics is reflected in their wide range of applications. From packaging and construction to healthcare and electronics, plastic plays a crucial role in our daily lives.
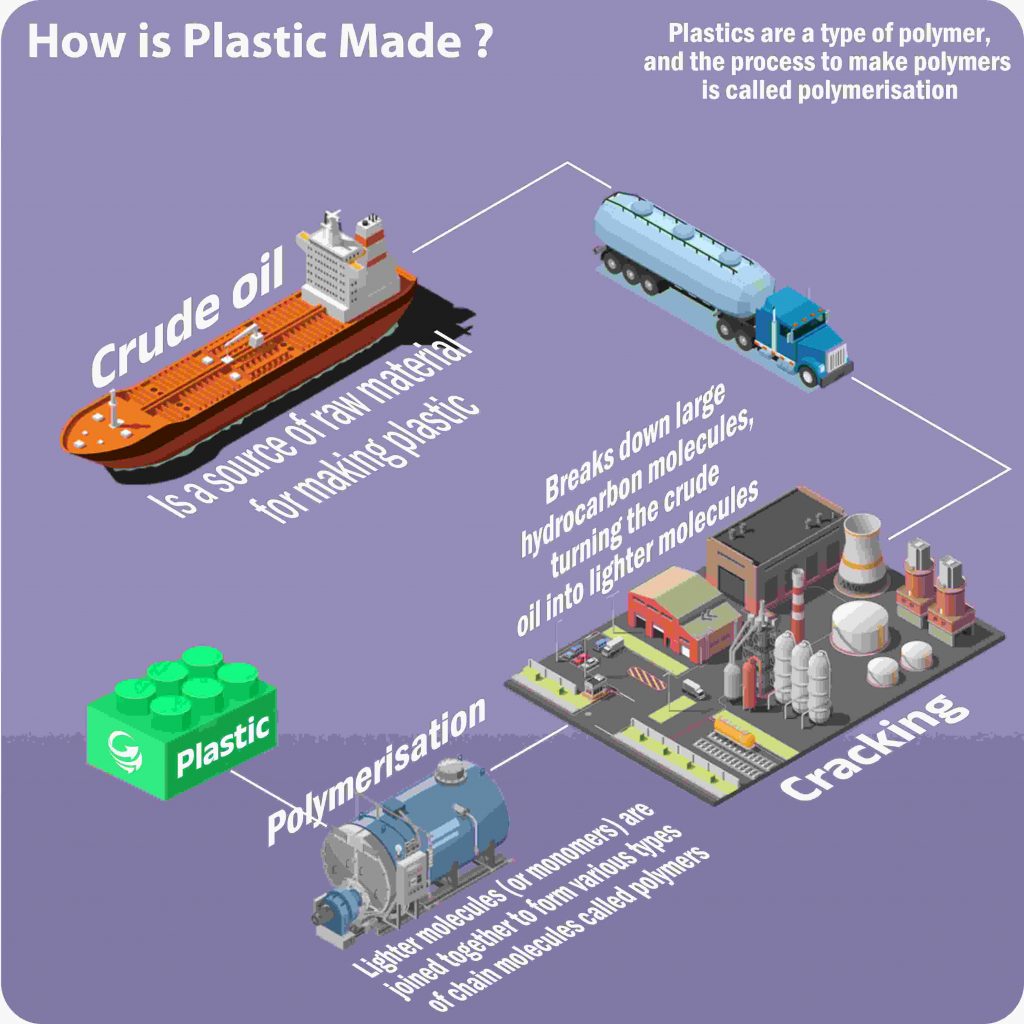
How is Plastic Made ?
Plastic is typically made through a process called polymerization, where small molecules (monomers) are chemically bonded to form long chains (polymers). This process allows for the creation of various types of plastic with unique properties.
Plastic materials are derived from petrochemicals like crude oil and natural gas. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of bio-based and eco-friendly plastics, reducing the environmental footprint.
History of Plastics
The history of plastics dates back to the mid-19th century, but it was the 20th century that witnessed the widespread development and use of synthetic plastics, revolutionizing industries and consumer products.
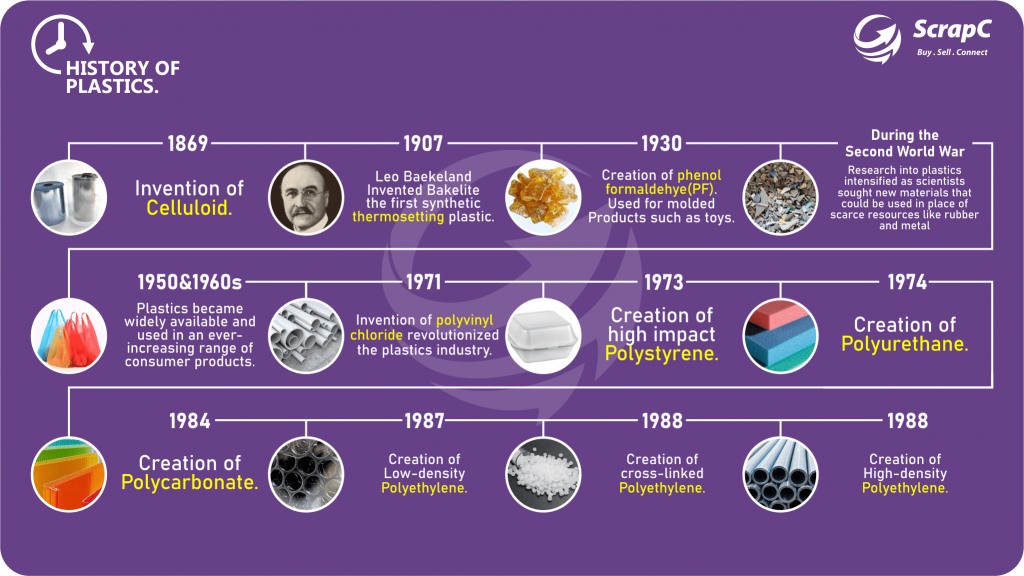
Plastic was invented by Belgian chemist Leo Baekeland in 1907. His creation, Bakelite, marked the beginning of the plastics era.
Plastic Waste Management
Plastic waste management involves the systematic handling, disposal, and recycling of plastic materials to minimize their environmental impact. This process aims to address the growing challenge of plastic pollution by promoting responsible consumption, efficient recycling infrastructure, and innovative solutions to reduce the overall burden of plastic waste on the planet. Effective plastic waste management includes collection, sorting, recycling, and proper disposal, fostering a sustainable approach to mitigate the environmental consequences associated with plastic materials.
Conclusion
Understanding the world of plastics, its types, and its impact on our environment is crucial. By making informed choices in plastic usage and promoting sustainable practices, we can contribute to a healthier and more eco-friendly future.